Frozen Desserts & Ice Cream
- Ice Cream Stabilizer
Ice cream is a frozen dairy product usually manufactured by freezing a mix stirred slowly to incorporate air, prevent large crystals formation, and ensuring a smooth texture.
The main objectives for using stabilizers in ice cream are to produce smoothness in body and texture, reduction in ice and lactose crystal growth during storage especially during heat shock, and to provide consistency to the product and opposition to melting shock.
Stabilizers added to ice cream perform numerous important functions, such as reduced whipping time, controlled fat destabilization, improved dryness, and increased resistance to melting and shrinkage

Stabilizer Blends
Gino offers a series of emulsifier and stabilizer blends (systems), tailored to meet the specific demands of Frozen Desserts & ice creams, and ice-lollies.
They are made from a combination of emulsifiers and hydrocolloids which are derived from red seaweed and other plant sources,
In certain (typically high-fat) foods like ice cream, it thickens, binds and stabilizes, a.k.a. keeps ingredients from separating.
It's also what gives your scoop a smooth consistency, and is packaged and low-fat foods, it makes them taste better.
- Key Benefits
- Improved form stability
- Production stability
- Improved melt-down properties
- Enhanced sensory properties
- Prevention of heat-shock
- Retard the formation of large ice crystals and large fat globules
- Improves texture and shelf life of ice cream.
- Specifications
| Items | Specifications | Test results |
| Appearance | Off white to yellowish powder | Qualified |
| Moisture (105℃) | ≤ 10 % | 6.7 |
| Total Ash (550℃) | 4.7 - 7.5 w/% | 5.6 |
| Viscosity (1.5%, 75℃) | 1000 - 2100 mPa·s | 2075 |
| pH(1.5%w/w, 55℃) | 7 - 9 | 7.5 |
| Lead (Pb) | Max 2 ppm | Qualified |
| Arsenic (As) | Max 2 ppm | Qualified |
| Total Plate Count | Max 20,000 CFU/g | 400 |
| Yeast and Moulds | Max 1,000 CFU/g | Qualified |
| E.Coli | Absent in 5 g | Qualified |
| Salmonella | Absent in 25 g | Qualified |
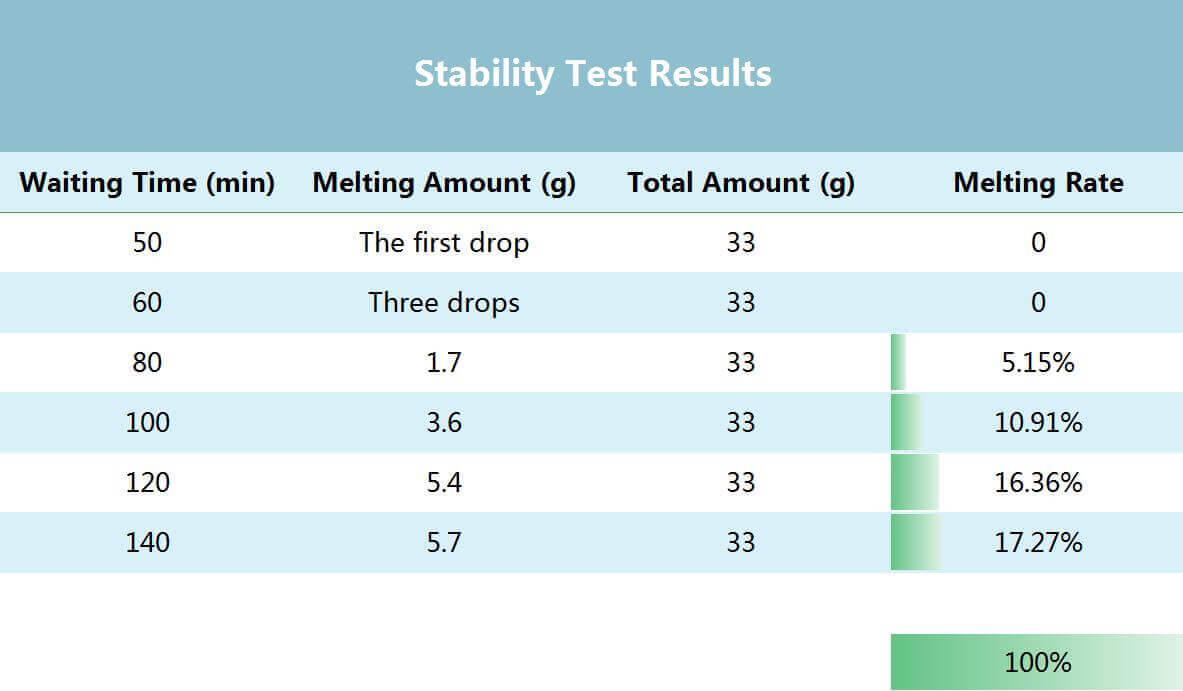
- Stability Test Results
- Relationship Between Ice Cream Composition And Stabilizer Concentration
The quantity of stabilizer and emulsifier required for different variety of ice cream differs based on the total solids, fat content, desired overrun etc.
As the fat level decreases, the amount of stabilizer/emulsifier concentration increases.
The reason is mainly attributed to decreased total solids content resulting in increased water concentration in the formulation.
As a result to attract water molecules in more numbers and to decrease bigger ice crystal formation, stabilizer/emulsifiers are added in more quantity (Arbuckle, 1986).
Examples of the approximate composition of some typical ice creams.
| Product | Milk Fat (%) | Solids not Fat (%) | Sweeteners (%) | Stabilizers and Emulsifiers (%) | Total Solids (%) |
| Non fat ice cream (hard) | < 0.8 | 12 - 14 | 18 - 22 | 1.0 | 35-37 |
| Low fat ice cream (hard) | 2-4 | 12-14 | 18-21 | 0.8 | 35-38 |
| Light ice cream (hard) | 5-6 | 11-12 | 18-20 | 0.6 | 35-38 |
| Economy ice cream | 10-12 | 10-11 | 15 | 0.5 | 35-37 |
| Frozen yoghurt | 3-6 | 8-13 | 15-17 | 0.5 | 30-33 |
| Soft serve ice cream | 3-4 | 12-14 | 13-16 | 0.4 | 29-31 |
- Functionalities Conclusion
Stabilizers afford functionalities that include:
- increased stiffness;
- provide a slower and more uniform meltdown;
- enhance whip ability during aeration;
- prevent lactose crystallization;
- prevent shrinkage during storage;
- stabilize the emulsion;
- contribute to body, texture, and creaminess.
Since all these properties cannot be met by a single hydrocolloid, it is always necessary for a stabilizer manufacturer to go for a blend that can meet the needs of the ice cream manufacturer.
Can't Find Your Application ?!
As one professional and experienced supplier and manufacturer in China,
Our technical sales representatives are able to assist product development and provide texture solutions
in common fields such as baking, dairy, meat and poultry, dressings, sauces, and confectionery.



