What is Low Acyl Gellan Gum E418: Safety, Properties, Benefits, Uses
What is Low Acyl Gellan Gum E418
1.What is Low Acyl Gellan Gum
Low acyl gellan gum (LA), also known as deacyl gellan gum or alkali-treated gellan gum, is obtained by removing all or part of the acyl group from the molecular structure of natural gellan gum (also known as high acyl gellan gum).
Low acyl gellan gum is a versatile and excellent gelling agent.
It can be dissolved in hot water or cold water (with chelating agent). Low acyl gellan gum has very high gel strength, high gel transparency, adjustable gel elasticity and hardness, superior flavor release, good compatibility, excellent thermal stability, acid resistance, enzymatic resistance, etc. at very low dosage.
Low acyl gellan gum can withstand high temperature treatment such as heating, sterilization, cooking, etc. It can be compounded into various gel structures, and can be made into thermally reversible gels or thermally irreversible gels according to the needs.
Low acyl gellan gum is widely used in food industry, which can extend the shelf life of acidic food, meet the requirements of many kinds of food with high transparency of gel, and help to develop new products, such as new texture, appearance or taste.

Is Low Acyl Gellan Gum Safe?
Gellan gum was first discovered in 1978 and was quickly approved by the US FDA for use in food and beverages in 1992, and by the European Community in 1994 when it was officially listed in the food safety code list (E418). In 1996, China approved its use as a food thickener and stabilizer (GB 2760-1996), which can be used in all kinds of food in appropriate amounts according to normal production needs.
2.Basic Information of Low Acyl Gellan Gum
| Chinese Name | 低酰基结冷胶 | Other Names | Deacyl Gellan Gum, Alkali treated Gellan Gum |
| English Name | Low Acyl Gellan Gum | Appearance | White powder |
| Molecular Weight | About 500,000 | Solubility | Dissolved in hot water or cold water (with chelating agent) |
| Gelation Conditions | Cations, acid, soluble solids | Gelation Temperature | 30-50℃ (86-122℉) |
| Thermally Reversible | Thermally stable | Sensitivity to Cations | Very sensitive, especially divalent cations |
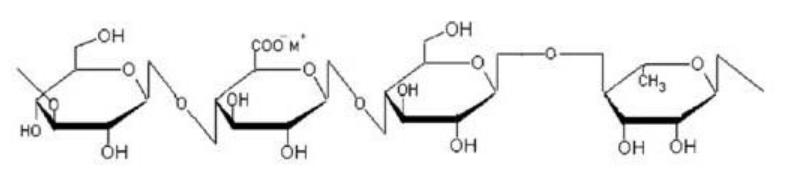
3.Low Acyl Gellan Gum Structure
Low acyl gellan gum VS High acyl gellan gum (natural gellan gum)
The main difference between the two structures is that the acyl group is partially or completely removed from the molecule of low acyl gellan gum, as shown in the figure below.
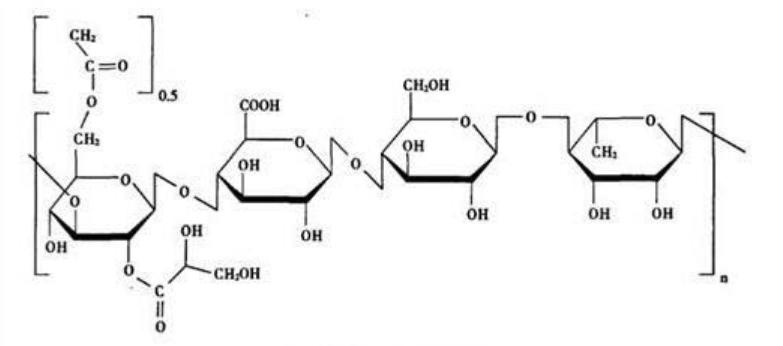
The molecular formula of high acyl gellan gum is shown in the figure below.
4. Production Method of Low Acyl Gellan Gum
- Alkali Treatment
- Rough Filtration
- Microfiltration
- Spray Drying
We treat the fermentation broth of gellan gum with alkali and then pass it through coarse filtration and microfiltration, and finally, the obtained gellan gum is spray-dried under pressure.
5.Low Acyl Gellan Gum Specification
NO. | ITEMS | SPECIFICATION |
1 | Appearance | White or off white, odorless powder |
2 | Gellan gum content | 85.0 %-108.0 % |
3 | Loss on drying | ≤ 15.0 % |
4 | Particle size | ≥ 95 % pass 60 mesh |
5 | Ph value | 5.5-7.5 |
6 | Ash | ≤ 15 % |
7 | Gel strength | ≥ 800 g/cm2 |
8 | Transparency | ≥ 76 % |
9 | Lead | ≤ 2 ppm |
10 | Mercury | ≤ 1 ppm |
11 | Arsenic | ≤ 2 ppm |
12 | Cadmium | ≤ 1 ppm |
13 | Total plate count | ≤ 5000 cfu/g |
14 | E. Coli | ≤ 30 MPN/100g |
15 | Salmonella | Negative |
6.Properties and Functions of Low Acyl Gellan Gum
- 1. The unique elasticity and gelling property of high acyl gellan gum make it can be applied in jelly, jam and sweet food.
- 2. High acyl gellan gum has thickening and stabilizing effect, which can be used in beverages, dairy products, ice creams, fillings, etc.
- 3. High acyl gellan gum has adhesive properties and can be used in frosting and icing.
- 4. High acyl gellan gum has strong water-holding property and can be used in cakes and cheeses to achieve moisturizing, freshness and shape preservation.
6.1 Characteristics of Low Acyl Gellan Gum Aqueous Solution
- Soluble in cold water and low ionic water (using chelating agent), the solution has viscosity
- Lower pseudoplasticity than xanthan gum solution, but higher than alginate solution
- Heating can greatly reduce the viscosity of the solution
- Very stable at pH 7 neutral conditions
- Low acyl gellan gum can be stable at 80℃ for about 1h
6.2 Hydration Properties of Low Acyl Gellan Gum
- Ionic (Ca, Mg, K, Na, etc.) content increases, and the temperature required for water solubility decreases.
- A multivalent chelating agent can reduce the temperature required for water solubility.
- Different multivalent chelating agents have different effective pH ranges and different buffering effects.
- Low pH increases the temperature required for water solubility.
- Sugar content increases the temperature required for water solubility.
- The process sequence is very important: put in the gellan gum with high-speed stirring first, then put in sugar, acid and ion, etc.
6.3 Gelling Properties of Low Acyl Gellan Gum
Low acyl gellan gum gel has the properties of high strength and brittle cracking, similar to those of carrageenan and agar, which are commonly used in industry.
Properties ( Advantages ) | Functions |
Low dosage: Works at very low dosage | Gellan gum is a very effective gelling agent, the dosage of gellan gum often ranges from 0.012% to 0.4% |
High transparency: The gels have high translucency | Gellan gum gels have excellent transparency and can meet the requirements of a wide range of food products with high gel transparency |
Acid stability: the formed gel is stable under acidity, especially at pH 4.0~7.5 | Satisfactory processing effect can be obtained from acidic to neutral product formulations, extending the shelf life of acidic foods |
Heat stability: the gels are thermally stable | Resistant to high temperature processing such as heating, sterilization, and steaming. |
Good synergistic effect: good compatibility with other hydrocolloids or ingredients | A variety of gel structures can be compounded, and can be transformed from brittle to elastic at will. |
Diverse gel structures: a variety of unique gel textures can be formed by changing the type and concentration of cations. Gels formed by monovalent ions (sodium or potassium ions) are thermally reversible, while those formed by divalent ions (calcium or magnesium salts) are thermally irreversible | Can be made into thermally reversible and thermally irreversible gels, as needed, to help develop new products with new textures, appearances or flavors |
Good suspending ability: weak gels also have good suspending properties | Can be used as a high-grade suspending agent |
Good flavor release: the resulting system has good flavor release | Jellies or air freshener gels made from gellan gum have good flavor release |
7. Properties Comparison of Low Acyl Gellan Gum and High Acyl Gellan Gum


| Low Acyl Gellan Gum (LA) | High Acyl Gellan Gum (HA) |
Molecular weight | 2-3@105 Daltons | 1-2@106 Daltons |
Solubility | Solubility in hot or cold water (with chelating agent) | Dissolved in hot water |
Gelation conditions | Cations, acids, soluble solids | Cooling |
Gel temperature | 30- 50°C (86-122°F) | 70-80℃ (158-176℉) |
Thermal reversibility | Heat stable | Thermally reversible |
Sensitivity to cations | Very sensitive, especially divalent cations (calcium, magnesium) | Not very sensitive |

8.Types of Low Acyl Gellan Gum
8.1 Gel Type Gellan Gum
Gel type gellan gum is mainly used in jelly, jam, candy and other water-based gel systems to play a gel forming role.
8.2 Culture-based Gellan Gum
It is mainly used in biological culture medium to form a solid and permeable medium to observe biological growth more clearly.
8.3 Daily Chemical Gellan Gum
It is mainly used in air scent and cosmetics to form a solid and permeable gel structure or emulsion with good water retention.
8.4 Suspension Type Gellan Gum
Suspension type gellan gum is mainly used in acidic or neutral high permeability suspension drinks, used to suspend fruit pulp, insoluble solid particles, to stabilize the beverage system, and can also be used alone to form a solid and brittle gel or mixed with other colloids to form a different structure of the product.
9. Uses of Low Acyl Gellan Gum
Low acyl gellan gum is widely used in food (such as beverages, jelly, jam, candy, etc.), daily products (air freshener gel), cosmetics, toothpaste and microbial culture media, etc.

9.1 Low Acyl Gellan Gum in Jelly, Jam and Candy
In jelly, jam, candy and other water-based gel systems, the use of low acyl gellan gum plays a gel forming role.
Recommended use amount: 0.1%-0.5%.
9.2 Uses of Low Acyl Gellan Gum in Biological Media
In biological medium, use low acyl gellan gum to form a solid and permeable medium to observe biological growth more clearly.
Recommended amount: 0.2%-0.8%.
9.3 Uses of Low Acyl Gellan Gum in Air Freshener and Cosmetics
In air freshener gels and cosmetics, low acyl gellan gum is used to form a solid and permeable gel structure or emulsion with good water retention & flavor release.
Recommended use amount: 0.2%-0.6%.
9.4 Uses of Low Acyl Gellan Gum in Suspension Beverage
In acidic or neutral high permeability suspension drinks, low acyl gellan gum is used to suspend fruit pulp, insoluble solid particles, to stabilize the beverage system, and can be used alone to form a solid and brittle gel or mixed with other colloids to form products with different structures.
Recommended use amount: 0.012%-0.03%.
10.History of Low Acyl Gellan Gum
The first gellan gum developed and produced was low acyl clarifying gum, which was widely used as gelling agent in the culture medium of thermophilic microorganisms in the early 1980s, because other existing gelling agents (e.g. agar) could not perform effectively at such high temperatures. The low acyl clarified gellan gum is very suitable as a gelling agent in plant tissue culture media because it has no undesirable impurities.


Applications and Prospects of High Acyl Gellan gum | Gellan Gum in Food
High acyl gellan gum powder can be used in neutral beverage applications at very low levels, with 0.02-0.05% recommended.