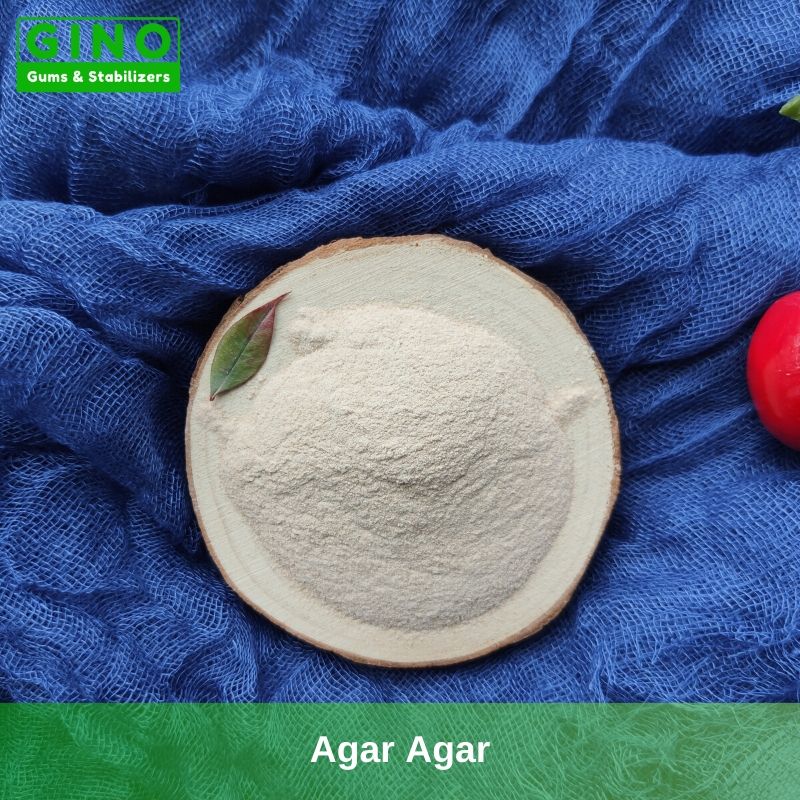
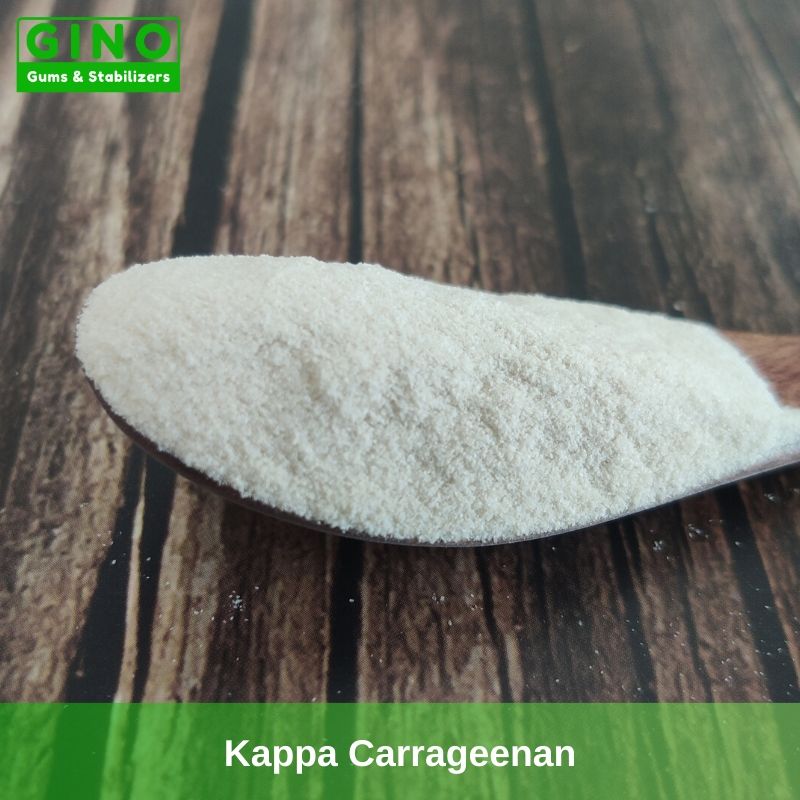
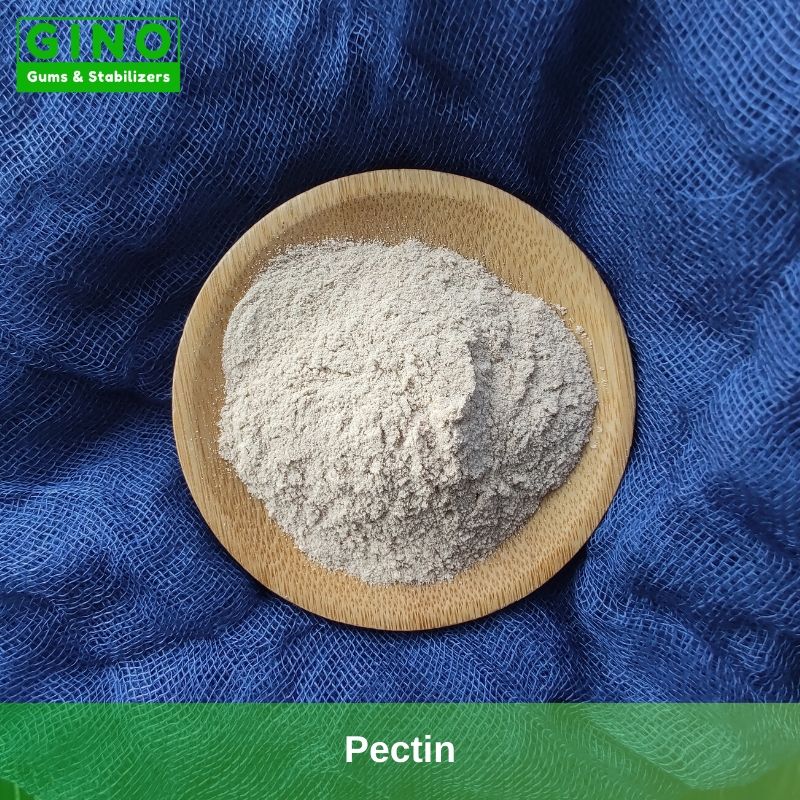
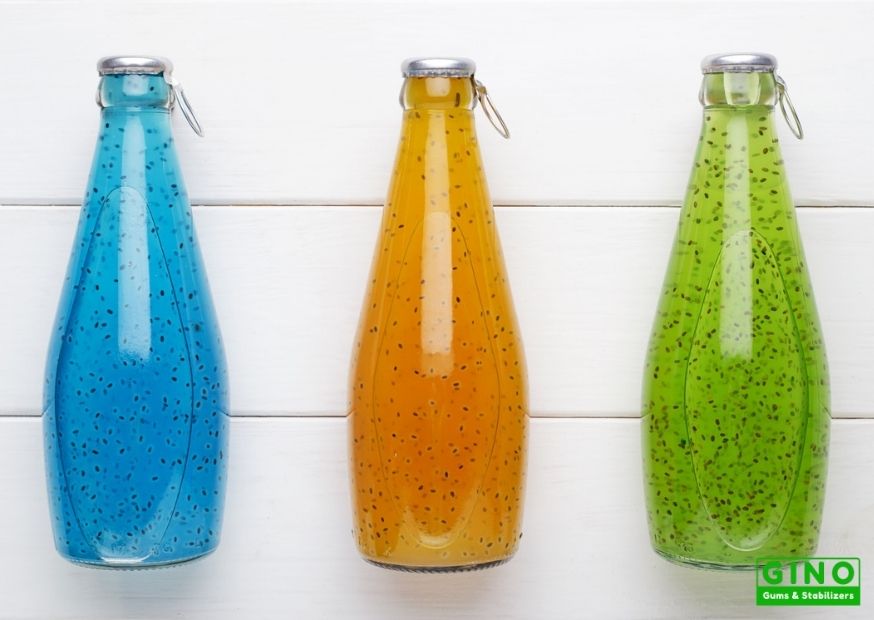
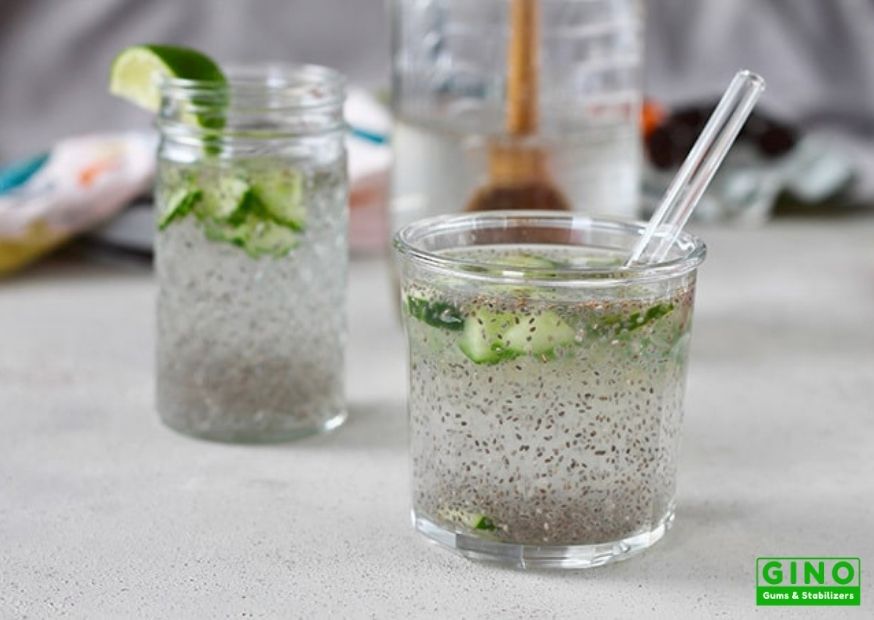
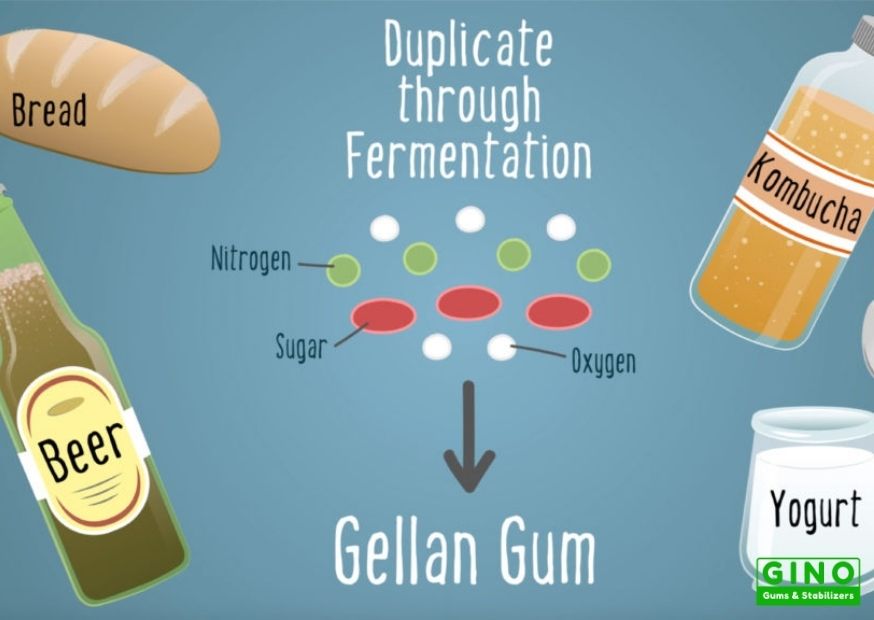
If you are looking for a trusted plant-based hydrocolloid supplier and food solution provider in China, Gino could be a better choice. We provide better ingredient options and the best solution to boost your business. Read More
Customer Focus
Products Development
Customized Packaging
Technical Support
Fast Service