The Ultimate Guide to High Acyl Gellan Gum E418
The Ultimate Guide to High Acyl Gellan Gum
1. What is High Acyl Gellan Gum? Gellan Gum Definition
High Acyl Gellan Gum, abbreviated as HA gellan gum, is also known as natural gellan gum or unalkalized gellan gum, which is obtained from the fermentation of Sphingomonas oligococcus without deacylation.
It is a dry, free-flowing, whitish powder that dissolves in hot water and has properties such as acid resistance, good water holding capacity, excellent suspension stability for pulp and insoluble components, and good compatibility with other hydrocolloids.
It can produce soft, elastic, and non-brittle gels, which can be mixed in a certain ratio or combined with other colloids to produce a variety of food products.
It has good structural recovery properties and excellent application properties in soy milk, milk kefir, yogurt, and chocolate dairy products.
- It can be used in baked dairy products and food fillings to increase the spice effect and have a stabilizing effect.
- In jam, it can make jam directly prepared with warm water and keep the system suspended and stable.
- In pastry, it can increase the elasticity and toughness of pasta products, reduce the breakage, improve the taste and make the taste more crisp and strong.
- It can be used in cakes, cheese and other desserts to achieve the effect of moisturizing, freshness and shape preservation.
- In addition, it can also be used in cold drinks, meat products and other food products.

2. Basic Parameters
Product Name | High Acyl Gellan Gum | Product Alias | Natural Gellan Gum, Unalkalized Gellan Gum, HA Gellan Gum, High Acyl GG |
Chinese Name | 高酰基结冷胶 | Appearance | Off-white to light yellow powder |
Particle Size(%) | 80 Mesh ≥98 | Solubility | Dissolve in hot water |
Gelation Condition | Cooling | Gelling Temperature | 70-80℃ (158-176℉) |
Thermal Reversibility | Thermally Reversible | Sensitivity To Cations | Not too sensitive |
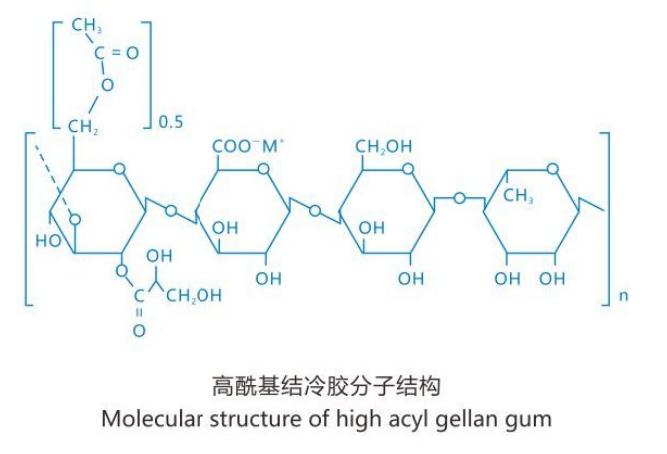
3. High Acyl Gellan Gum Chemical Structure
HA gellan gum has an average of 1 acyl group on each repeating unit of (1,3)β-D-glucose, which is divided into two types of acyl groups, namely acyl and glycerol acyl, attached to the 6th and 2nd carbon atoms of the glucose residue, respectively, with the average ratio of glycerol acyl groups being twice that of acyl groups.
The presence of acyl and glycerol acyl groups in the molecule makes the HA gellan gum exhibit different gel properties than the low acyl gellan gum.
4. Specification
Appearance: Off-white to light yellow, tasteless, liquid powder
Content: 85-108%
Solubility: Soluble in water to form a viscous liquid, insoluble in ethanol
Calcium ion test: pass
Sodium ion test: pass
Particle Size: 80 mesh through≥95%
Loss on Drying: ≤15.0%
Ash: ≤15.0%
pH: 5.0-7.0
Residual Alcohol: ≤750mg/kg
Gel strength: ≥1000g/cm2
Viscosity (CP): ≥6500cp
Nitrogen(%): ≤3%
Lead (Pb): ≤2mg/kg
Arsenic (As): ≤3mg/kg
Mercury (Hg): ≤1mg/kg
Cadmium (Cd): ≤1mg/kg
TPC (CFU/g): ≤10000cfu/g
Coliforms (MPN/100g): ≤30MPN/100g
Yeasts and molds (CFU/g): ≤400 cfu/g
Salmonella: 0/25g
We herewith confirm that the ingredient of our product is 100% food-grade Gellan gum (INS No.418) and is suitable for human consumption.
We hereby confirm that the ingredients of HA gellan gum meet the quality and purity requirements of FAO/WHO JEFCA for the identity and purity of a Food Additive as per the above specification.
E Number | Ingredients | CAS Number | % |
E418 | Gellan Gum | 71010-52-1 | 100 |
5. High Acyl Gellan Gum Production Process
In brief, firstly, adjust the pH of fermentation broth to 4-4.5, raise the temperature to 90℃, maintain it for 10-30min, inactivate the enzyme to kill the bacteria, then add 2%-3% of fermentation broth volume of electrolyte solution, react for 30min, finally add isopropyl alcohol solid-liquid separation, solid state for vacuum drying.
Incubation of Pseudomonas elodea
↓
Seed Culture
↓
Fermentation
↓
Acid out and Filtering
↓
First Time Separation
↓
Second Time Separation
↓
Drying
↓
Milling
↓
Screening(60-80 mesh)
↓
Blending for Homogeneous
↓
Packaging
↓
Metal Detecting
↓
Finished Product
CCP1: Seed Culture
- Yeast extract
- Fish peptone
- White granulated sugar
- Sodium chloride
- Sodium hydroxide
CCP2: Acid out and Filtering
- Hydrochloric acid
Download The Full Production Process
Click Here6. Packaging and Storage
25kg kraft paper drum lined with a sterile plastic bag, inner packaging material meets food-grade contact material regulations and food safety standards. Store in a cool, dry place, and avoid light exposure. The shelf life is 24 months under sealed conditions

7. Quality System
Gellan Gum has passed ISO9001:2015 quality management system, ISO22000:2005 food safety management system certification, and has obtained KOSHER and HALAL certificates.
8. Laws and Regulations
The product complies with GB2760, GB25535-2010, FCCV, and FAO/WHO standards.
9. High Acyl Gellan Gum Properties

9.1 Solubility Properties
When gellan gum is dissolved in water, the molecules will automatically gather between them to form a double-stranded helix structure, and the double helix can further gather to form a three-dimensional mesh structure.
Ions have a great influence on the swelling temperature, and sodium ions increase the swelling temperature. The viscosity of the hot solution is higher than that of the low acyl gellan gum, which is very stable under neutral conditions at pH 7, and the high acyl gellan gum can be hydrolyzed under acidic pH 3.5.
High acyl gellan gum can show very high viscosity when dispersed in cold water, but it is more sensitive to salt solution, which limits the application of high acyl gellan gum as thickener to some extent.
At the same time, high acyl gellan gum sols have high thixotropy.
9.2 Sol-gel Transition Properties
The sol-gel transition mechanism determines the gel properties of HA gellan gum, such as structural stability and rheological properties.
Different acyl content of HA gellan gum also leads to different sol-gel transition properties, and the lower the acyl content, the more obvious the temperature hysteresis and the lower the gel temperature.

9.3 Gel Properties
9.3.a Weak Gel Properties
Due to the different structures, high and low acyl gellan gum show different gel characteristics.
High acyl gellan gum can form thermally reversible gels without cations, and when cations are present, free acyl bonds can interact to form sparse intermolecular crosslinks.
Low acyl gellan gum forms hard and brittle gel at 25℃, while high acyl gellan gum chain forms soft and elastic gel at 72℃ with no temperature hysteresis.
However, high acyl gellan is more conformationally ordered than low acyl gellan gum at high temperatures and is more stable than low acyl gellan gum in double helix structure formation and aggregation.
HA gellan gum exhibits weak gel properties.
9.3.b Rheological Properties
The high acyl GG shows high yield strain and yield stress, while Young's modulus is low, which also indicates that the high acyl GG forms soft, elastic gels.
The hard and brittle gels formed by the low acyl gellan gum indicate that the glycerol acyl group has a stabilizing effect on the three-dimensional structure of the high acyl GG.
It was found that the flexible chains in high acyl GG occupy a smaller hydrodynamic volume than the non-flexible ones when measuring the characteristic viscosity of high acyl GG.
With the increase of shear rate, the high acyl GG exhibits pseudoplastic fluid properties.
9.3.c Water Holding Properties
Gel water-holding property is an important parameter of gel properties, and the level of gel water-holding property directly affects its textural properties and product cost.
High acyl gellan gum can maintain 84% water holding capacity after 60 min centrifugation under different calcium ion concentration.
The high water-holding capacity of high acyl GG is related to the presence of more hydrogen bonds in the main chain of the double helix, while the insensitivity to calcium ions may be due to the altered ionic bonding properties of glycerol acyl groups.
9.3.d Stability Properties
The high acyl GG can still have good spatial reticulation gel under the external shear effect of small changes, still can play a good role in suspension and stabilization, and has good shear resistance.
At the same time, gellan gum has high viscosity at a low shear rate and at rest, so it has good transportation performance and shelf stability.
10. Properties and Functions of High Acyl Gellan Gum (Non-Clarifying Type)
High acyl GG non-clarifying type is a multifunctional edible gelling agent with gelling, stabilizing, and film effects.
10.1 Properties
- Shear reversible gels
- Heat reversible gel
- Excellent flavor release properties
- Can be used with other hydrocolloids
- Synergistic with starch
- Excellent conformability
- Elastic gel
- Enhances mouthfeel
10.2 Properties of Aqueous Solutions
- Dissolving in cold nonionic water, sodium ions increase the swelling temperature
- Its gel structure contributes to high viscosity
- Heating causes a large decrease in viscosity
- The hot solution has a higher viscosity than low acyl gellan gum
- Very stable at pH 7 neutral conditions
10.3 Hydration Properties
- Ions have a strong influence on the solubilization temperature
- Ions have a slight effect on the hydration temperature
- Dissolves in the water below 100°C
- High solids increase the required temperature of aqueous solutions
- pH reduces the required temperature of the aqueous solution
- Feeding sequence is important: first put in high acyl non-clarifying gellan gum with high speed stirring in hot water, then put in sugar, acid, ions, etc.
11. Low Acyl Vs High Acyl Gellan Gum
The acyl group has a very significant effect on the properties of the gellan gum.
The high acyl group produces soft, elastic, and non-brittle gels, while the low acyl group produces firm, non-elastic, but brittle gels.

Comparison - Properties of Low Acyl Acyl Gellan vs High Acyl Gellan Gum
Molecular weight | 2-3@105 Dalton | 1-2@106 Dalton |
Solubility | Dissolve in hot or cold water (with a chelating agent) | Dissolve in hot water |
Gelling conditions | Cation, acid, soluble solids | Cooling |
Gel temperature | 30-50℃ (86-122℉) | 70-80℃(158-176℉) |
Thermally reversible | Thermally stable | Thermally reversible |
Sensitivity to cations | Very sensitive, especially divalent cations | Not very sensitive |


12. High Acyl Gellan Gum Uses in Food
It is one of the best thickeners and stabilizers with excellent performance in the market and has superior gel characteristics.
Compared with other edible colloids, it has good flavor release, high thermal stability, good water-holding, suspension, and thermally reversible flexibility.
These properties make it wide and superior in application.

Its solubility is relatively weak to cation sensitivity, it can be used with monovalent and divalent soluble salts, the suspension and stability of the colloid also need the auxiliary effect of cation, the solubility temperature is above 85℃, the applicable pH range is 3.4-7.5.
It is often used in non-transparent beverages or food, such as dairy products, cereal drinks, vegetable protein drinks, fresh juice or vegetable juice drinks, health drinks, meat products, etc.
Can also be used in combination with CMC, guar gum, microcrystalline cellulose, pectin, carrageenan, and other colloids to broaden its scope of application.
12.1 High Acyl Gellan Gum in Beverages & Dairy

12.1.1 Neutral Milk Beverages
It can be used directly in dairy products.
In neutral dairy products, 0.025%-0.035% of high acyl GG can be used alone with a certain amount of sodium or calcium salt as a stabilizer, which can achieve the effect of suspension of solids and elimination of flocculation, and has the characteristics of thickening, refreshing and so on.
12.1.2 Acidic Milk Beverages
In acidic milk beverages or other dairy products, 0.02%-0.03% of high acyl GG can be compounded with 0.2%-0.4% of sodium hydroxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and then used in combination with a certain amount of calcium salts as a stabilizer, in which CMC is used as a protective agent and high acyl GG can play the role of suspension of solids, thickening, and stabilization.
12.1.3 Fermented Yogurt
In fermented yogurt, it can be compounded with a certain amount of guar gum as a protective agent to prevent protein flocculation and precipitation.
In dairy products, it is used instead of carrageenan, gelatin, alginates, and pectin, and has the advantages of solubility with casein - low reactivity, no wall formation, low dosage, good structural recovery properties, etc.
12.2 High Acyl Gellan Gum in Fruit Juices & Suspension Beverages
Compared with xanthan gum, it has superior acid and salt resistance and a wide range of stability, which can be better reflected in acidic fruit juices and non-transparent suspension beverages.

12.2.1 Acidic Fruit Juices
In acidic fruit juices, the amount of high acyl GG added is only 1/7-1/8 of xanthan gum to achieve the same stabilization effect, and it has obvious advantages over xanthan gum in beverage conditions and tastes.
12.2.2 Suspension Beverages
Compared with other colloids with suspension performance, IT has a very low addition amount of 0.025% without other colloids in the beverage suspension with large pulp.
Moreover, compared to carrageenan, pectin, guar gum, etc., its the pH range in suspension systems can be applied in acidic and neutral suspension beverages.
Properties and Applications of High Acyl Gellan Gum in Food
Properties | Applications |
Gelling properties | Jellies, fillings, sweets, jams, etc. |
Stabilizing | Beverages, dairy products, ice cream, salad dressings, etc. |
Thickening | Jam, sausage, stuffing, etc. |
Viscoelasticity | Pasta products |
Adhesion | Sugar icing, sugar coating |
Film coating | Preserves, candies |
Water holding | Desserts (e.g. cakes, cheesecakes, etc.) |
12.3 High Acyl Gellan Gum in Plant Protein Beverages
Plant protein beverages are the fastest-growing soft drink industry in recent years.
Plant protein beverages use plant nuts and pulp as the main raw materials, and their protein and vitamin contents are high, so they are high-end products in the beverage industry.
At present, the stabilizers used in the production of plant protein beverages are basically several colloids compounded together, the ratio parameters and application methods are relatively strict, and the general loss of colloid performance after high-temperature sterilization is relatively large.
High acyl GG used in plant protein drinks not only has good high-temperature resistance but also has the role of thickening and stabilizing protein.
The recommended dosage is 0.03%-0.04%. It can also be used in combination with other hydrocolloids, such as: carrageenan, guar gum, acacia bean gum, etc. The synergistic effect can also achieve good stabilization effect.
12.4 High Acyl Gellan Gum in Cereal Beverage
Cereal beverages have been developing quite rapidly in recent years.
Cereals are rich in insoluble fiber, which plays an important role in the health of the human digestive system and blood system, so more beverage manufacturers have been developing cereal beverages in recent years.
The basic process route of cereal beverages is as follows: cereal soaking - maturation - grinding - stabilizer addition - homogenization - pasting - sterilization - filling.

Although the process is relatively simple, the requirements for stabilizers are also relatively high, and the poor choice of stabilizers can easily lead to flocculation and precipitation, water separation, and other problems.
The starch content in the cereal beverage system is high, and the consistency itself is relatively large, therefore, the dosage of added colloid should not be too large, otherwise, it will affect the taste, but it should also play a stabilizing role.
Compared with other colloids, high acyl gellan gum can meet the above requirements, and the addition amount is as low as 0.025%, with good stabilization effect, and it is suitable for pasteurization and high temperature sterilization procedure of beverage.
12.5 High Acyl Gellan Gum in Meat Products
Most of the traditional meat products such as ham sausage, sausage, and pork chops use carrageenan, xanthan gum, or gelatin as excipients to stabilize the structural and organizational state.
In recent years, more manufacturers are using HA gellan gum as an excipient for meat products.

Compared with other colloids, HA gellan gum has better temperature resistance, water retention, and elasticity in ham sausage, which makes the system richer and has a more pleasant taste.
In meat steaks, the high viscosity of HA gellan gum can better bind the meat pieces and make the meat steaks have a richer eating effect.
13. High Acyl Gellan Gum Benefits

- Excellent thickening
- Excellent suspension performance
- Good acid thermal stability
- Good taste
- Good compatibility
14. Prospects of High Acyl Gellan Gum in Food Industry
It is a microbial extracellular polysaccharide with important commercial value, which has been researched and developed for its short production cycle, not restricted by climate and geographical environment conditions, safe and non-toxic, unique physicochemical properties, etc. Based on its superior gelation properties, it has a wide application prospect in food, pharmaceutical, chemical, and other fields.
At present, low acyl gellan gum has been relatively widely used in the food industry, while the lack of research on high acyl GG has limited its application.
However, the unique gel properties of HA gellan gum can provide excellent texture and taste, high water-holding capacity can improve the water-holding capacity of food in storage, and good compatibility with other food gums can enhance food stability and improve tissue structure to obtain the best textural characteristics.
15. Research and Limitations of High Acyl Gellan Gum in China
In recent years, with the gradual research on HA gellan gum, its superiority in a variety of food and beverage applications has been gradually recognized, but it is still not well promoted.
The factors that restrict the application of HA gellan gum are as follows.
- Domestic development research started late, compared with LA gellan gum, the process technology of HA gellan gum is more demanding
- Fewer manufacturers produce HA gellan gum in China
- Domestic enterprises do not have sufficient research on the characteristics and application of HA gellan gum
- The difficult technology causes high production costs and high market prices. Although the superiority of the application is more, the higher cost also makes many users discouraged.
These factors have seriously restricted the application of HA gellan gum.
However, the superiority of high acyl gellan gum application is being recognized by more and more users, and domestic production and development are also developing rapidly, and it is believed that in the near future, the production process of HA gellan gum will be more mature and the application research will be more extensive.
Looking for high-quality gellan gum?
Looking for high-quality gellan gum for your food, beverage, or pharmaceutical applications?
At Gino Gums, we offer premium high-acyl and low-acyl gellan gum products that deliver excellent texture, stability, and performance across a wide range of formulations. Whether you're developing plant-based beverages, desserts, or dietary supplements, our gellan gum solutions can meet your needs.
📩 Contact us today to request samples, technical data, or pricing information - let us help you find the right gellan gum for your next innovative product!
📞 [Contact Us] | 📦 [Request a Sample] | 💬 [Get a Quote]
Contact us today