Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan: A Comprehensive Comparison for Better Understanding
Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan

There are numerous options available for food hydrocolloids, each with distinct properties and applications. Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan are two hydrocolloids frequently utilized in the food industry as gelling agents, thickeners, and stabilizers. Despite their similarities, there are significant distinctions between the two additives.
To gain a better understanding of these two additives, this article will provide a comprehensive comparison between them.
1. What is Gellan Gum
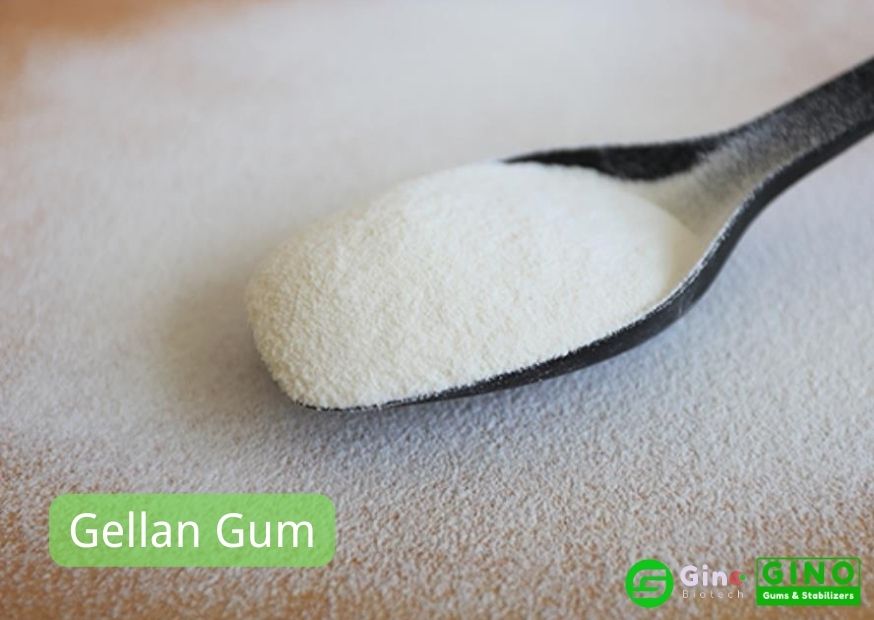

Gellan Gum is a polysaccharide that is produced by the bacterium Sphingomonas elodea.
The usage of this substance in the food industry dates back to the 1990s, but it was actually discovered in the 1970s.
Gellan Gum is a versatile additive that can form a wide range of textures, from soft gels to firm gels and even fluid gels. It is also heat-stable, which makes it suitable for use in hot applications, such as baked goods.
2. What is Carrageenan

Carrageenan is a polysaccharide that is extracted from certain species of red seaweed. It has been used in the food industry for centuries and is a popular additive due to its gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties. Carrageenan can be used to form soft gels, but it is not as versatile as Gellan Gum when it comes to forming firm gels.
3. Types of Gellan Gum and Carrageenan
3.1 Gellan Gum Types: Gellan gum also has different types, but the most commonly used type in food applications is high acyl gellan gum.
- High acyl gellan gum forms a soft, elastic gel and is commonly used in dairy products, such as yogurt, as well as in confectionery products and sauces.
- Low acyl gellan gum forms a firm, brittle gel and is often used in combination with other hydrocolloids to create textures such as gel-like coatings and glazes.
3.2 Carrageenan Types: Carrageenan comes in three main types: kappa, iota, and lambda carrageenan, each with unique properties and uses.
- Kappa carrageenan is known for its ability to form a firm and rigid gel when mixed with potassium ions, making it a popular ingredient in confectionery, jelly, dairy products like ice cream and chocolate milk, as well as in processed meats and pet food.
- Iota carrageenan forms a more soft and elastic gel when combined with calcium ions, making it a popular choice for desserts such as jellies and puddings, as well as in dairy products like yogurt.
- Lambda carrageenan does not form a gel but is used as a thickener and stabilizer in many food products, such as canned pet food and chocolate milk.
Overall, both gellan gum and carrageenan have different types with unique properties and uses, allowing for a wide range of applications in the food industry.
4. Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan: A Comprehensive Comparison
Now that we have introduced both additives, let's take a closer look at how they compare.
4.1 Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan: Comparison of Sources & Production

Gellan gum is produced by a bacterium called Sphingomonas elodea, which ferments glucose or other simple sugars. The bacteria produce long chains of repeating glucose molecules, which are then purified and dried to create gellan gum. Gellan gum is considered a natural, microbial-based ingredient and can be produced using a relatively simple fermentation process.
In contrast, carrageenan is extracted from red seaweed, which is harvested and washed in seawater to remove sand and other impurities. The seaweed is then chopped and boiled in an alkaline solution to extract the carrageenan. The extracted carrageenan is then further processed and refined to remove impurities and create a standardized product. The process of extracting carrageenan can be more complex and labor-intensive than producing gellan gum, and it is also more dependent on the availability and quality of the seaweed crop.
Additionally, some people have concerns about the sustainability and environmental impact of carrageenan production, particularly if the seaweed is harvested in an unsustainable or environmentally damaging way. Gellan gum, on the other hand, is produced using a fermentation process that can be controlled and optimized to reduce environmental impact.
Overall, while both gellan gum and carrageenan are used as gelling agents and stabilizers in food and other applications, they differ in terms of their sources, production processes, and environmental impact.
4.2 Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan: Comparison of Properties
- First, their gelling properties are different. Gellan gum gels at a much lower concentration than carrageenan, which makes it a more efficient gelling agent. Additionally, gellan gum forms firm, brittle gels, while carrageenan forms softer, more elastic gels. This difference in texture can impact their use in various applications. For example, gellan gum is commonly used in dairy products and jellies because it creates a firmer texture, while carrageenan is often used in water-based products, such as beverages, because it creates a smoother, more gel-like texture.
- Second, their solubility is also different. Gellan gum is soluble in both hot and cold water, while carrageenan requires heat to dissolve. This makes gellan gum more versatile in its use, as it can be used in cold applications without needing to be heated first.
- Third, their stability under different conditions is different. Gellan gum is more stable under acidic conditions than carrageenan, which can break down under acidic conditions. This makes gellan gum a better choice for acidic products such as fruit gels and acidified dairy products. On the other hand, carrageenan is more stable under alkaline conditions, making it a good choice for use in products that have a higher pH.
In summary, gellan gum and carrageenan differ in their gelling properties, solubility, and stability under different conditions. These differences can impact their use in various applications, and understanding these differences is important when selecting the appropriate hydrocolloid for a particular product.
4.3 Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan: Comparison of Advantages
Both gellan gum and carrageenan have unique advantages that make them useful in different applications.

- Gellan gum, for example, is known for its ability to form strong, elastic gels at low concentrations, making it a popular choice in the food industry for a wide range of products such as desserts, sauces, and beverages. In addition to its gelling properties, gellan gum also has excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for use in hot or cold products.
- Carrageenan, on the other hand, has been used for centuries as a thickening and stabilizing agent in a variety of food products. Carrageenan's ability to form a gel in the presence of calcium ions, as well as its ability to emulsify and stabilize, make it a popular choice in products such as ice cream, yogurt, and dairy alternatives. Carrageenan also has a unique mouthfeel and can improve the texture and overall sensory experience of food products.
In terms of advantages, gellan gum has a few key benefits. For one, it has excellent stability under a range of pH and temperature conditions, making it a versatile ingredient that can be used in a wide range of products. It is also easy to use and can be added to products at low concentrations. Additionally, gellan gum can be used to create clear or translucent gels, making it a popular choice for products where visual appearance is important.
Carrageenan also has several advantages. Carrageenan, which is derived from seaweed, is a natural and approved ingredient used in non-GMO and organic products. It is an effective thickener and stabilizer, requiring low concentrations that can save manufacturers money. It is compatible with various ingredients, and it can be used in vegan and plant-based products.
Overall, both gellan gum and carrageenan have unique advantages that make them useful in different applications. Manufacturers must consider the properties and uses of these ingredients when selecting which one to use in their products.
4.4 Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan: Comparison of Price & Market Demand
In terms of price, gellan gum is generally more expensive than carrageenan.
Gellan gum is often pricier than carrageenan because it is a newer and less widespread ingredient in the food industry, whereas carrageenan has been commonly used for many years and is more widely available.
In terms of market demand, both carrageenan and gellan gum are used as thickening and stabilizing agents in a variety of food and beverage products. However, carrageenan has faced some controversy in recent years due to concerns about its safety and potential health effects, which has led some companies to look for alternatives.
As a result, there has been increasing interest in gellan gum as a carrageenan alternative, particularly in the natural and organic food markets. This has led to a growing demand for gellan gum, although it is still not as widely used as carrageenan.
Overall, the market demand for both carrageenan and gellan gum is driven by the need for functional ingredients that can provide specific texture and stability properties in food and beverage products. While carrageenan has a long history of use and wider availability, gellan gum is becoming more popular as a carrageenan alternative, particularly in the natural and organic food markets.
4.5 Gellan Gum vs Carrageenan: Comparison of Application
Gellan gum and carrageenan are both food additives that are commonly used to provide texture and stability to a variety of food and beverage products.

- Gellan gum is a polysaccharide that is known for its strong gelling ability, good syneresis control, and good heat stability. This makes it suitable for products that require a firm texture, good stability, and high-temperature processing. Some examples of products that may use gellan gum include desserts, jams, jellies, sauces, dressings, and baked goods.
- Carrageenan, on the other hand, is a polysaccharide derived from red seaweed that is known for its ability to thicken and stabilize liquids, as well as its water-binding, emulsifying, film-forming, and texturizing properties. Carrageenan has weaker gelling properties than gellan gum, but it is compatible with acidic ingredients, making it suitable for use in dairy, fruit, and vegetable beverages, as well as plant-based milk alternatives. However, carrageenan has limitations in highly acidic conditions and is not recommended for use in products that require high stability or processing at high temperatures.
In summary, the choice between gellan gum and carrageenan will depend on the specific properties required for the end product and any limitations or restrictions on their use. Gellan gum is best suited for products that require a firm texture, good stability, and high-temperature processing, while carrageenan is best suited for products that require thickening, stabilization, or a range of other textural properties, and is compatible with acidic ingredients.
Here are some common applications for each additive
Gellan Gum:
- Jellies and puddings
- Dairy products (such as yogurt and sour cream)
- Baked goods (such as cakes and muffins)
- Confections (such as gummies and marshmallows)
- 반려동물 사료
- Culture media
- 음료
Carrageenan:
- Jellies and puddings
- Dairy products (such as ice cream and whipped cream)
- Deli meats and processed meats
- Confections (such as chocolate milk and fruit gels)
- 반려동물 사료
- Culture media
- 음료
결론
In conclusion, both gellan gum and carrageenan are important food additives that provide unique textural and stability benefits to a wide range of food and beverage products. Ultimately, understanding the differences between gellan gum and carrageenan can help food manufacturers make informed decisions about which additive to use for their particular application.
?? ???
MCP 시리즈 12: 개량 감귤 펙틴은 왜 그렇게 비싼가? 원가 공개
MCP 시리즈 11: 필요에 맞는 다양한 유형의 개량 감귤 펙틴 살펴보기
MCP 시리즈 09: 변성 감귤류 펙틴 중금속 해독
회사 소개
더 건강한 삶을 위한 식물성 잇몸 및 안정제를 제공한다는 사명을 가지고 2018년에 설립된 지노 검스 앤 스태빌라이저.
우리는 다양한 종류의 식물 기반 하이드로콜로이드 및 안정화 솔루션 시스템에 주력하고 있습니다.