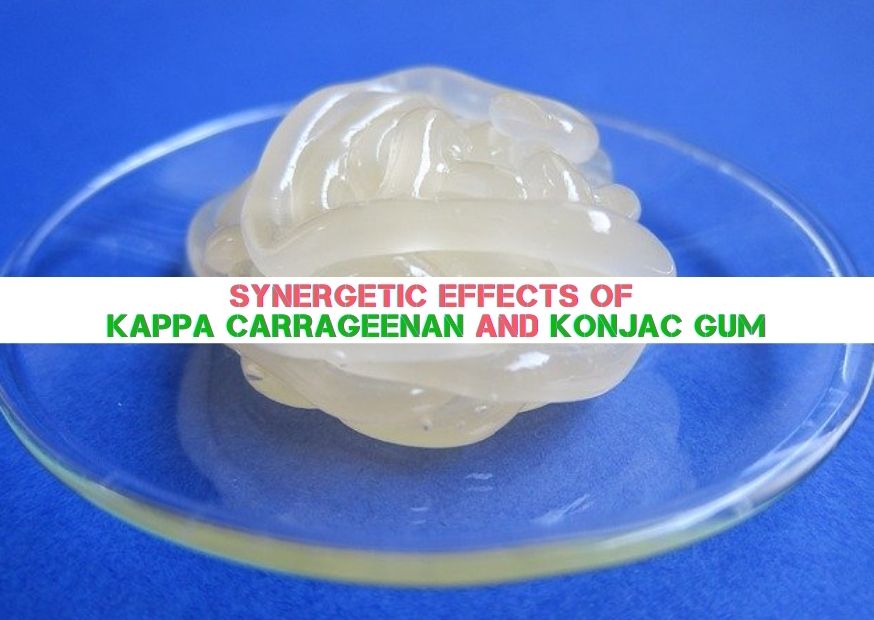
The Magical Synergetic Effects of Kappa Carrageenan and Konjac Gum
Synergistic Effects of Kappa Carrageenan and Konjac Gum
카파 카라기난 그리고 konjac gum are both commonly used as gelling agents in the food industry, their synergistic effects can significantly improve their own defects.
1.What is Kappa Carrageenan?
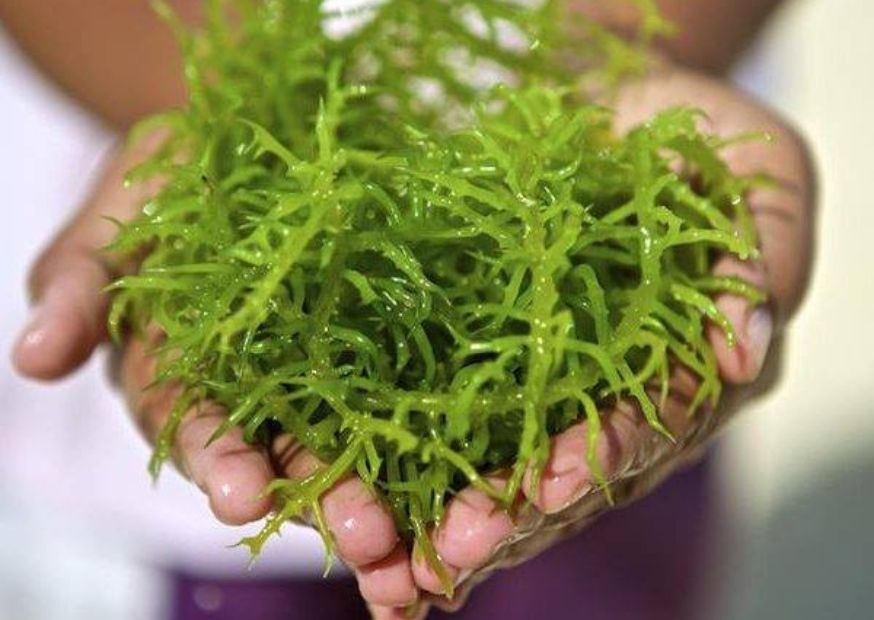
Carrageenan is a sulfated polysaccharide polymer extracted from certain species of red algae. Depending on the content and location of the sulfate group in the structure, there are seven types of carrageenan, including kappa, iota, lambda, theta, mu, nu and ksi, all of which contain 22% to 35% sulfate group. Kappa carrageenan is the most common and widely used.
Kappa carrageenan is extracted from algae of the genus Kirin, and is obtained by drying, alkali treatment, water washing, acid bleaching, water washing, boiling, filtering, cooling, pressing and dehydration, drying and grinding.
K-carrageenan has the best solidifying property among all types of carrageenan.
Because of its unique characteristics such as thermo-reversible gelation, anti-protein coagulation, hydrophilic and non-toxic, biodegradable and low cost, it has attracted much attention in food, chemical, packaging, pharmaceutical and edible cling film.

2.What is Konjac Gum?
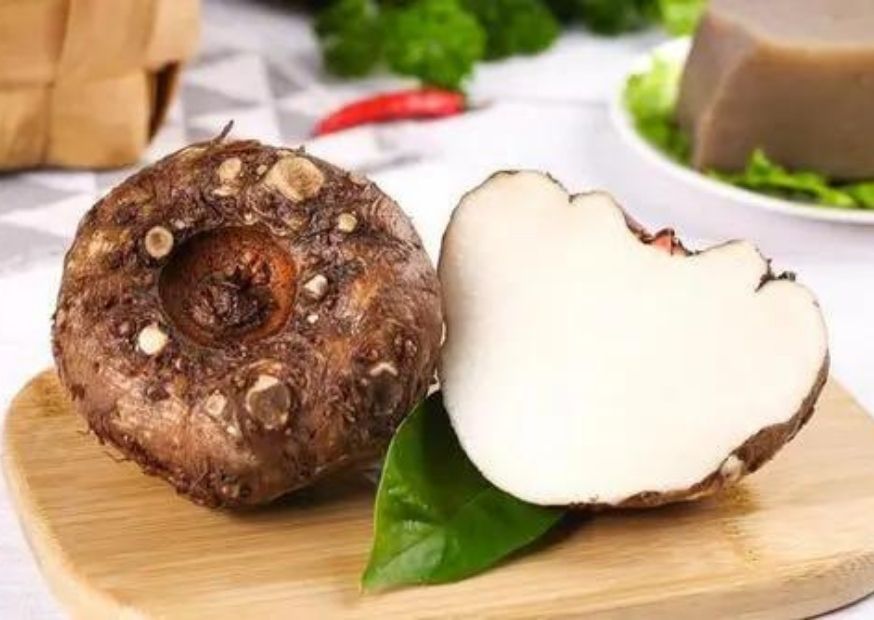
The main chemical composition of konjac gum is glucomannan, in which the molecular ratio of glucose and mannose is about 2:3, because there is an acetyl group on the 6th C of the mannose unit, so its aqueous solution can not form a gel, but in dilute alkaline solution after hydrolysis to remove the acetyl group can form an elastic gel.

3.Disadvantages
Kappa carrageenan and Konjac gum are both commonly used as gelling agents in the food industry, however, both of them have different degrees of disadvantages and shortcomings.
3.1 Carrageenan Disadvantages
Kappa carrageenan in the presence of potassium or calcium plasma, has the advantages of low concentration required to form a gel, high transparency, but its gel brittle, elasticity is small, prone to shrinkage off the liquid phenomenon.
3.2 Konjac Gum Disadvantages
Konjac gum must be at a concentration of 2% or more, pH>9 i.e. strongly alkaline conditions to form a gel.
In addition to the large amount, the application of alkaline food often has a salty and astringent taste, poor taste, not popular;
These defects, to a large extent, affect the two as a gelling agent in the food industry applications.
4. Synergistic Effects of Kappa Carrageenan and Konjac Gum
Konjac gum can fully or partially replace locust bean gum, and obtain the gel structure of the mixture of carrageenan and locust bean gum.
- Low use level of gelling agent
- High gel strength
- Low water separation rate (Low syneresis)
Konjac gum can fully or partially replace locust bean gum, and obtain the gel structure of the mixture of carrageenan and locust bean gum.

5. 결론
In conclusion, kappa carrageenan and konjac gum have a strong synergistic effect, can significantly enhance the gel strength and elasticity of carrageenan, improve the water separating properties (syneresis) of carrageenan, the effect is stronger than locust bean gum, and has good application value in the food industry.

The 4 Major Differences Between Carrageenan and Konjac Gum You Should Know
Do you know the differences between Carrageenan and Konjac Gum?
?? ???
MCP 시리즈 12: 개량 감귤 펙틴은 왜 그렇게 비싼가? 원가 공개
MCP 시리즈 11: 필요에 맞는 다양한 유형의 개량 감귤 펙틴 살펴보기
MCP 시리즈 09: 변성 감귤류 펙틴 중금속 해독
회사 소개
더 건강한 삶을 위한 식물성 잇몸 및 안정제를 제공한다는 사명을 가지고 2018년에 설립된 지노 검스 앤 스태빌라이저.
우리는 다양한 종류의 식물 기반 하이드로콜로이드 및 안정화 솔루션 시스템에 주력하고 있습니다.